Game playing introduction in artificial intelligence
Tags:
WEEK-2 Game playing with AI
Game playing with AI is hard. We look for strategies for turn based games
- Game we pick is Isolation. Player1 starts with ‘O’
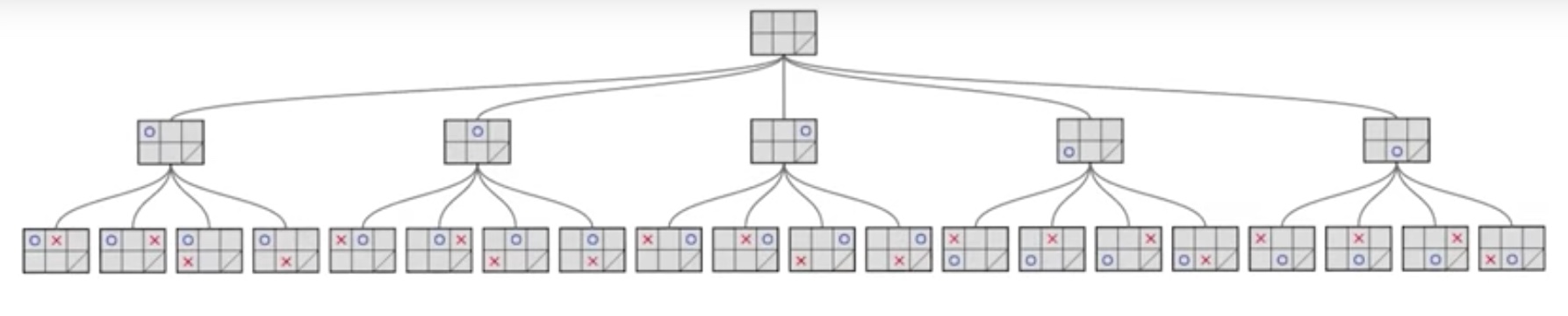
- Build a tree of all possiblities. Find the branches where player1 will loose.
- Teach computer to find loosing branches with a version of MiniMax algorithm.
Max number of nodes visited.
- for 5 x 5 board of isolation game, at each turn number of available branches are ,
25 * 24 * 23 * ... * 3 * 2 * 1 = 10^25. Not feasible.
Branching factor
- Consider branching factor. After each player turn no of empty boxes decreases. When P1 starts it has max 16 places for second turn. After this it has max of 12 option to play. No of available branch
25 x 24 x 12^11 x 5e8 ~ 3e23 - Average branching factor. Find number of branches at each level and divide it by level. Play the game for multiple time. Avg branching is ~8.
- Time taken to find sol with avg branching factor is
8^25 ~= e22 ~ 1.22 million yrs. - We can limit the depth of our branching to 2 sec (UX).
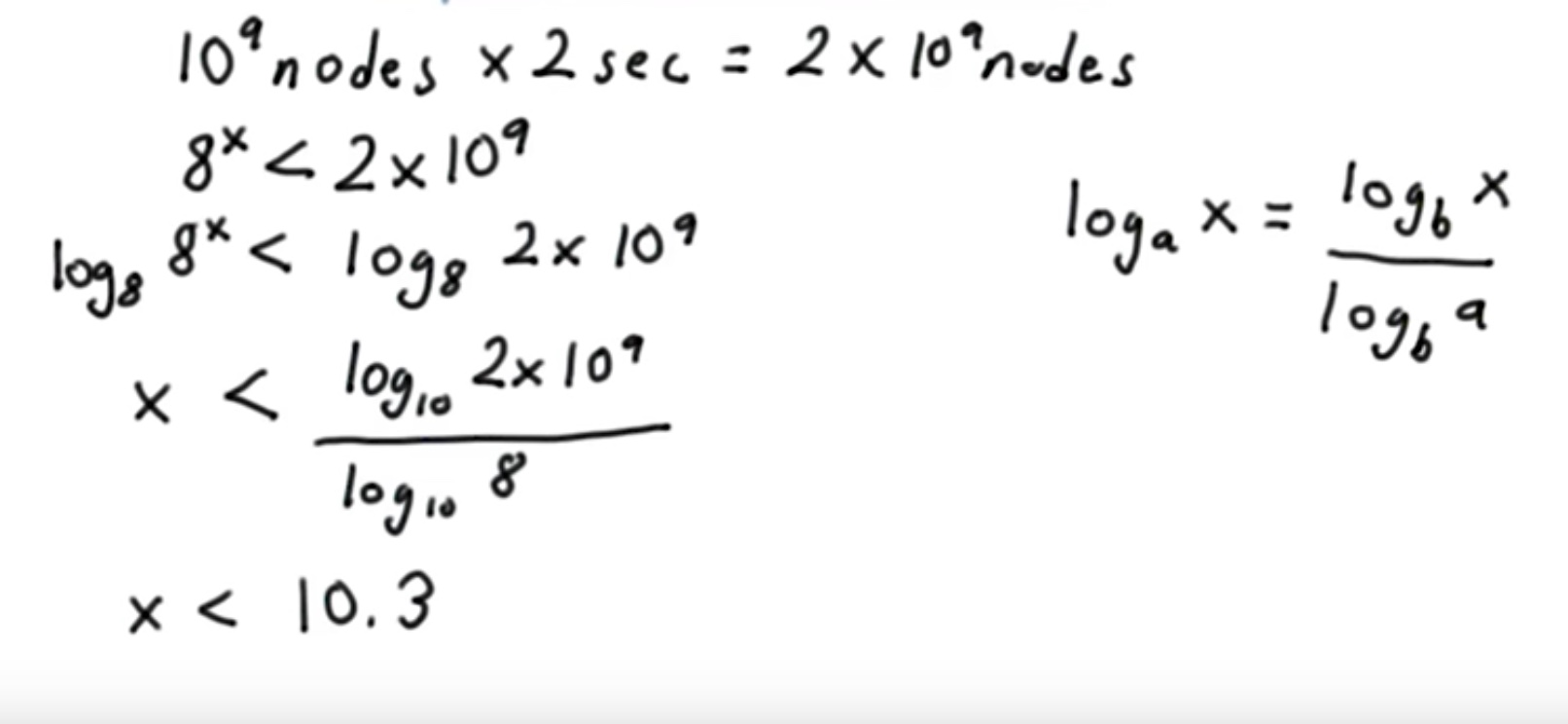
- We assume we have 9 level to compute in 2 sec.
Evaluation Fun & Quiescent Search
- We need to know at level 9 which player has most boxes to play. We call this evaluation fun and pass it to minimax algo.
- The result of evaluation fun will change and it depends on the level at which evaluation fun starts.
- The idea of quiescence is that the static evaluator should not be applied to positions whose values are unstable, such as those occurring in the middle of the piece trade. In those positions, a small secondary search is conducted until the static evaluation becomes more stable. In games such as chess or checkers, this can be achieved by always exploring any capture moves one level deeper. This extra search is called quiescence search. Applying quiescence search to capture moves quickly will resolve the uncertainties in the position.